What does GCSE stand for?
GCSE stands for General Certificate of Secondary Education and provides an academic qualification in different subject areas.
They are an essential step for students as they provide a foundation for higher education and career development.
What level is a GCSE?
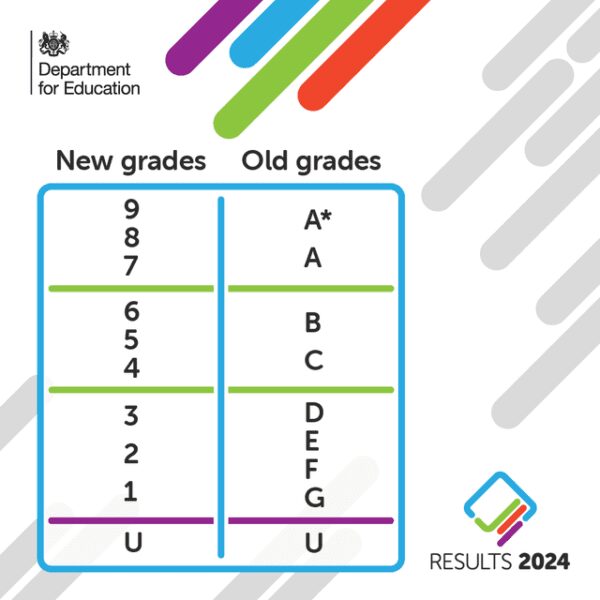
GCSEs are part of key stage 4 and traditionally, were graded from A* to G. However, this changed in 2017 and they are now graded from 9-1. For comparison, 9 is the equivalent of a high A*.
GCSEs that are graded 3, 2, or 1 are considered a level 1 qualification in the UK’s National Qualifications Framework. Level 2 is for grades 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, and 4, which indicate an intermediate level of education, providing students with a broad and balanced curriculum.
What year do you take your GCSE?
In most UK schools, students choose their GCSE options in Year 9 and typically begin their courses in Year 10. This usually lasts for two years, with exams taking place at the end of Year 11 – the final year of secondary school.
The GCSE period is crucial for students as it shapes their academic journey and influences their future educational and career paths.
Which GCSE subjects are mandatory?
Although some of your GCSE subjects can be your own choice, there are compulsory national curriculum subjects. The ‘core’ subjects are English Literature and Language, Maths, and Science, and the ‘foundation’ subjects are computing, PE, and citizenship.
Schools must also offer at least one in the four ‘entitlement’ areas; the arts, humanities, design and technology, and modern foreign languages. The rest of the optional subjects are then entirely dependent on what the school offers and what the student decides.
How many GCSEs do you have to take?
The amount of GCSEs a student takes again varies from school to school. This usually ranges from a minimum of 5 to a maximum of 12 GCSEs.
Students should choose subjects based on their interests and whether they are relevant to their future career goals.
What are the GCSE Exam Boards UK?
There are several exam boards in the UK offering GCSE qualifications. The five prominent ones are AQA, CCEA, OCR, Edexcel, and WJEC.
Each exam board sets its own syllabus and exams but all adhere to the national curriculum guidelines. Though these exam boards differentiate between schools, they are also all overseen by regulatory authorities to ensure equality between schools. These are OfQual (England), DCELLS (Wales), and CCEA (Northern Ireland).